Sometimes we find that we have the data that we store or retrieve from an application out of order, without any logical order, and we need to organize and/or classify it to process it correctly or use it more efficiently.
With the Master of Advanced Programming in Python, Hacking, Big Data and Machine Learning You will be able to become a widely qualified expert to carry out programming work in Python specialized in cutting-edge areas such as Big Data, Hacking and Machine Learning.
Types of sorting algorithms in Python
Today we are going to learn about the most common sorting algorithms:
- Bubble Sort
- Selection order (Sort Selection)
- Insertion Type (Insert Sort)
- Merge Sort
Bubble Sort
This simple sorting algorithm iterates over the list of data, comparing elements in pairs until the largest elements “bubble” to the end of the list and the smallest ones remain at the beginning.
Start by comparing the first two list items, if the first element is greater than the second, we exchange them, if not, they stay as they are. Then we move on to the next pair of elements, compare them and swap if necessary.
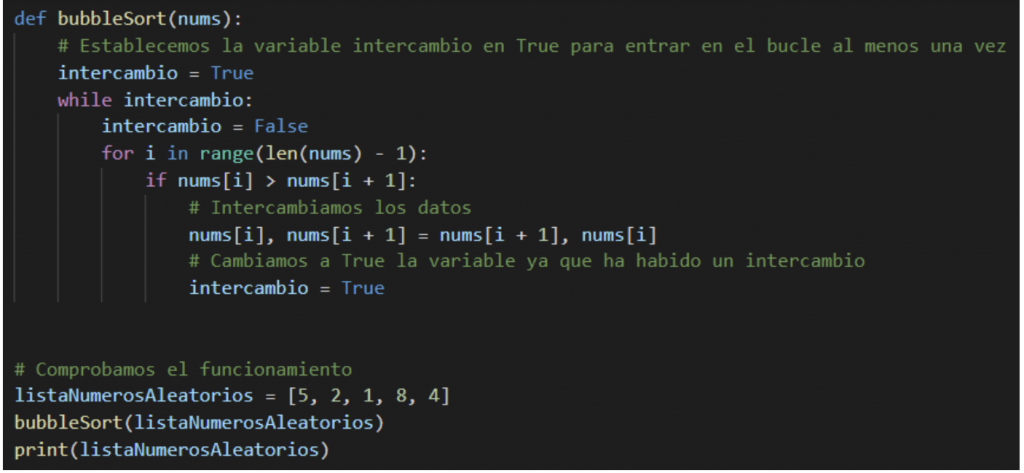
The while loop breaks when no elements have been swapped.
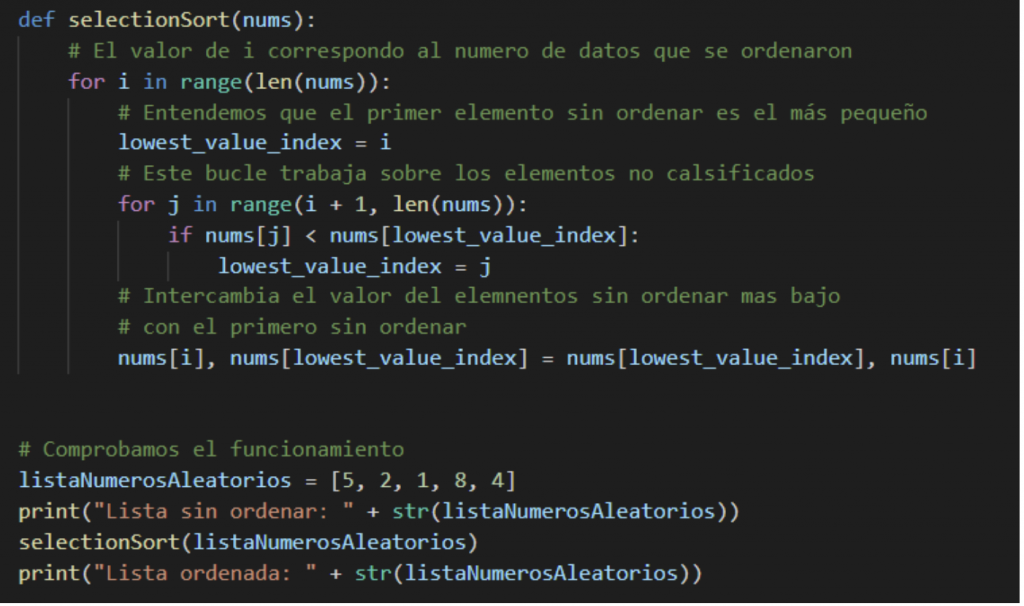
Selection order (Sort Selection)
This algorithm separates the list into two parts, ordered and not ordered. It continually “removes” the smallest element from the unsorted part and adds it to the sorted part.
What this algorithm actually does is treat the left part of the list as the sorted part by searching the entire list for the smallest element and putting it first. Then, knowing that we already have the smallest element first, we search the entire list for the smallest of the remaining unordered elements and exchange it with the next ordered one and so on until the list is finished.
The more elements we have ordered, the fewer elements we will have to examine.
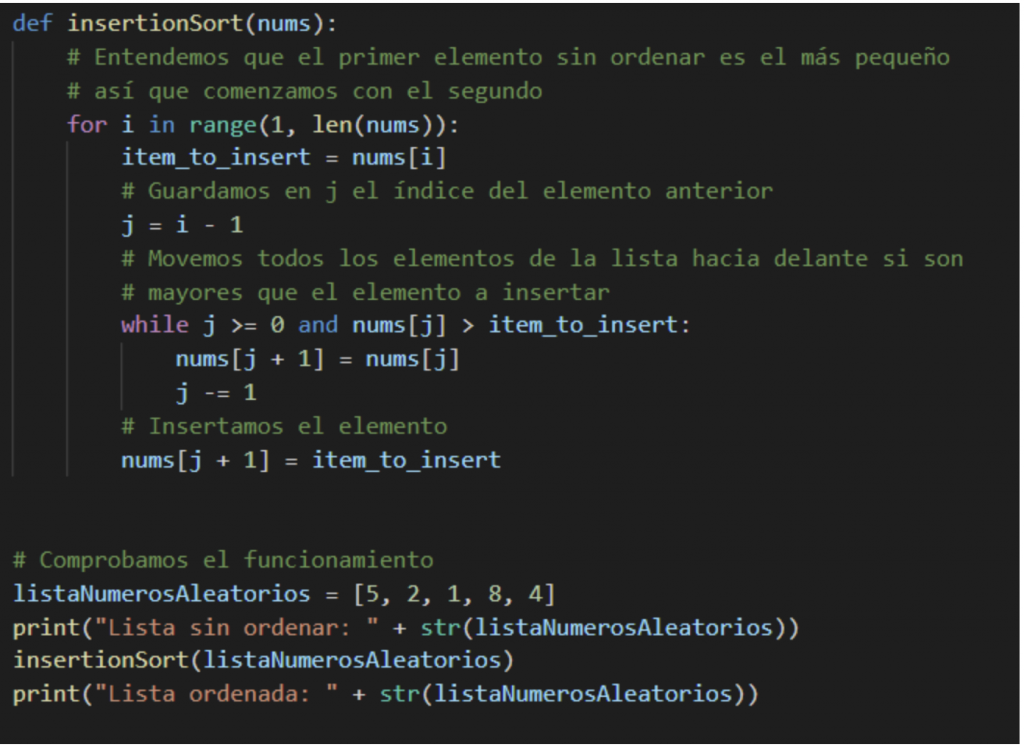
Insertion Type (Insert Sort)
This algorithm, like selection sorting, separates the list into two parts, ordered and unordered. We also assume that the first element is sorted, then we go to the next element that we are going to call X, we compare we insert X as first.
Merge Sort
This algorithm starts splitting the list into two, then those two halves into 4 and so on until we have lists one element long. These elements are then put back together in order. We'll first merge the individual elements into pairs again by sorting them with each other, then we'll continue sorting them into groups until we have a single sorted list.
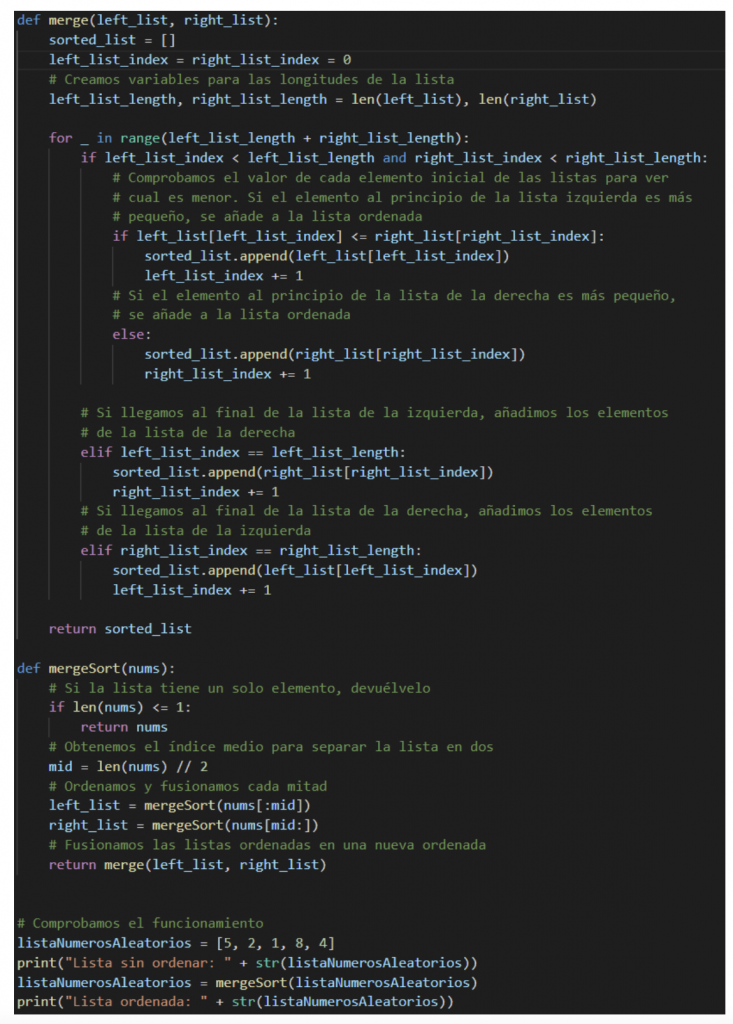
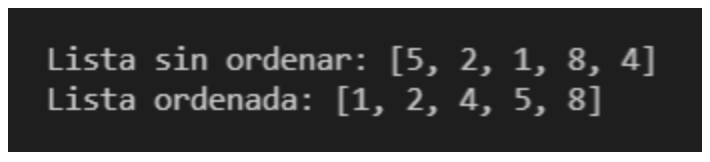
He result with any of the algorithms it would be the following:





































this sucker! I would repeat
The web designer should be very proud of how landspace looks on mobile. Quality your! 😓
The insertion algorithm does not give that result, unless the first element is the smallest, ex: 1, if it is another number it does not sort it.