Using JavaScript objects (JSON) is a powerful tool for quickly exchanging data between various programming platforms. Whether storing data or creating an API, converting your data to JSON makes it reusable, regardless of the technology accessing it.
Below we explain how to read and write to a JSON file in Python.
To become a highly qualified expert in this field in just 12 months, the Master of Advanced Programming in Python for Hacking, Big Data and Machine Learning It will train you so that you obtain the necessary skills.
Difference between a JSON object and a Python dictionary
The difference between a JSON object and a Python dictionary is minimal, therefore it is easy to store a Python dictionary as JSON. But to make it work, we need the parser library json .
We are going to learn basic knowledge of using JSON files in Python. To start, we create a JSON file in the root directory of our project.
We create and open a Python file in the same directory and with this we can write a dictionary in the file JSON Using our Python code:

How do we store a list as JSON in Python?
Sometimes we may have one or more lists and we want to save them as JSON. A good way to do this is to convert them into dictionaries before writing them to the file. JSON.

If we want to merge two lists before writing them to the file JSON We can do it with the use of FOR loops in the following way:
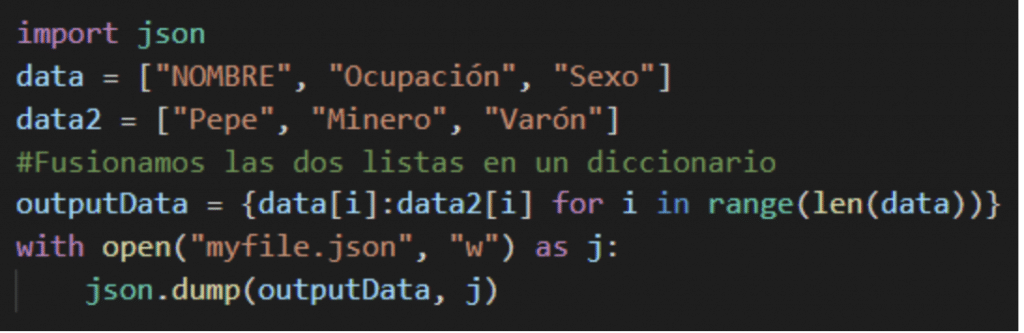
Access JSON data
Access and consult file data JSON It is very simple
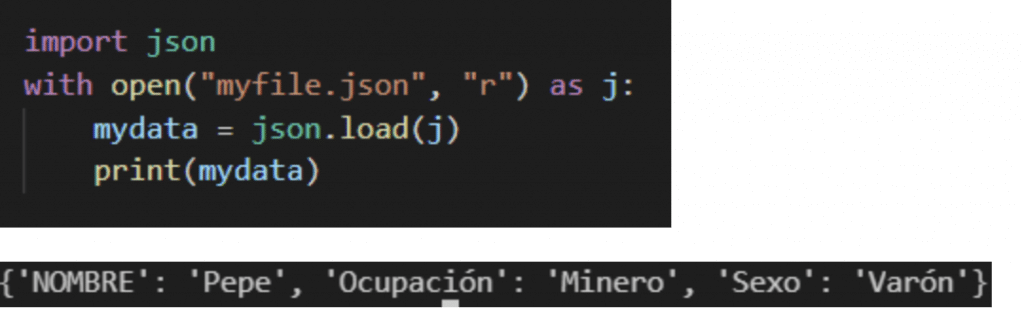
And if we want to obtain more specific data we can indicate it.
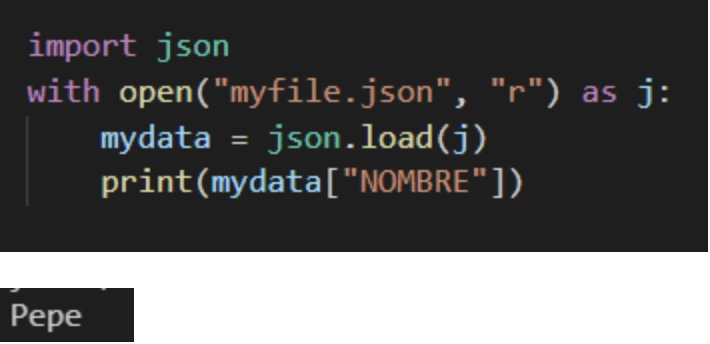
Quick queries in Python with JSON
The objects JSON In addition to being multiplatform, they are very lightweight and can improve the speed of response to our queries and, as we have seen, review the data in the files. JSON in Python it's pretty simple.







































Thanks.