Among the many types of Data structures that Python has, there are the lists. A list in Python is a data structure made up of an ordered sequence of objects, which do not have to be of the same type.
exist many methods to work with lists, here we are going to show you some of them, if you want to learn more about lists and become a professional in Python, train with our master in Advanced Programming in Python for Big Data, Hacking and Machine Learning and stand out from the rest.
In Python lists are very flexible and it does not require that the elements of the list have to be of the same type ('int', 'float', 'chr', 'str', 'bool', 'object'), as occurs in other programming languages.
To create a list in Python, we must place all the elements that we want to add to that list between square brackets [ ] and separated by commas.
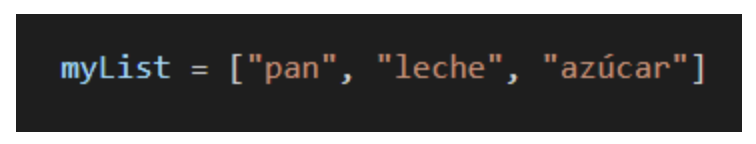
Lists can contain as many items we want and as we already said, they can be of different types (integers, strings, booleans, etc.)
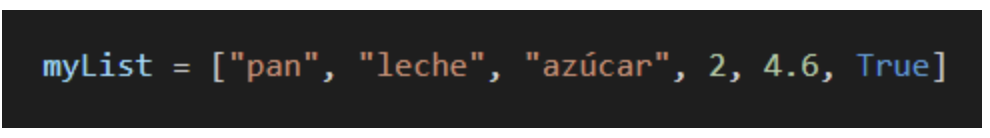
Lists can also contain other lists, which will count as a single value within the list.

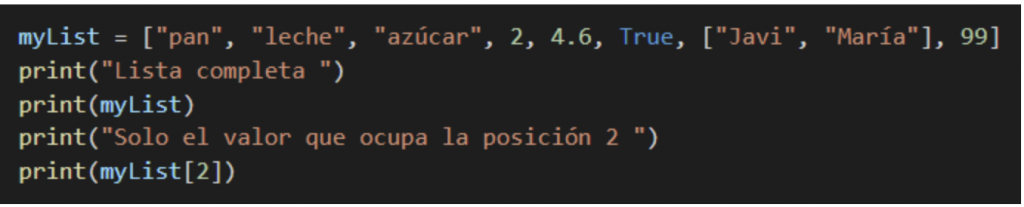
In order to see the created list or a specific item in the list, we can use the index, always knowing that the first element of the list occupies position 0.

List Methods
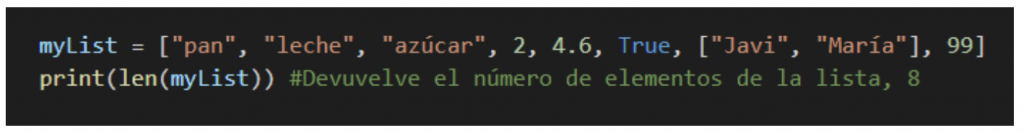
len()
This method returns us the length of an object, in this case when used on the list, it will return the number of data that comprises it.
Index()
Returns the position of the element that we have entered for your search, if there were two identical elements, it would only return the position of the first.

Append()
This method adds a element at the end of the list. In the example we see the list before and after adding the new data, in our case we have added the data “milk” and a list again.
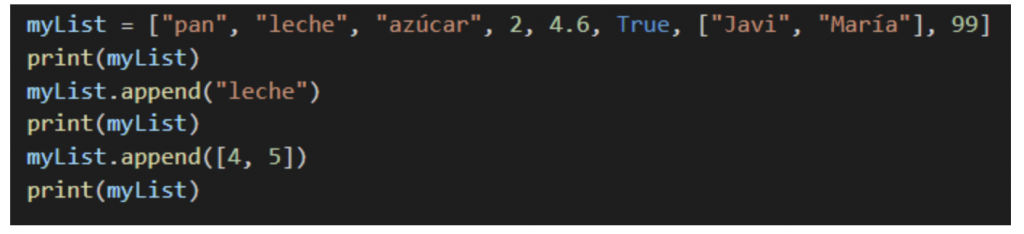
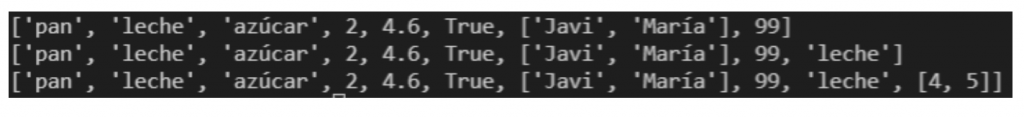
Count()
With this method we can know the number of times an item is repeated in our list.
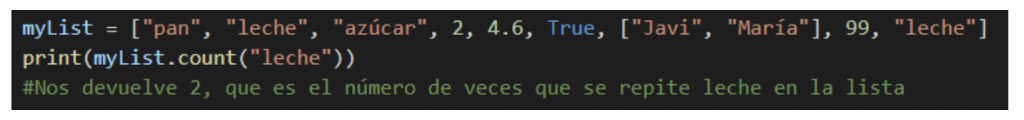
Extend()
With this method we can add elements from one list to another but unlike append(), as new elements inside the new list.
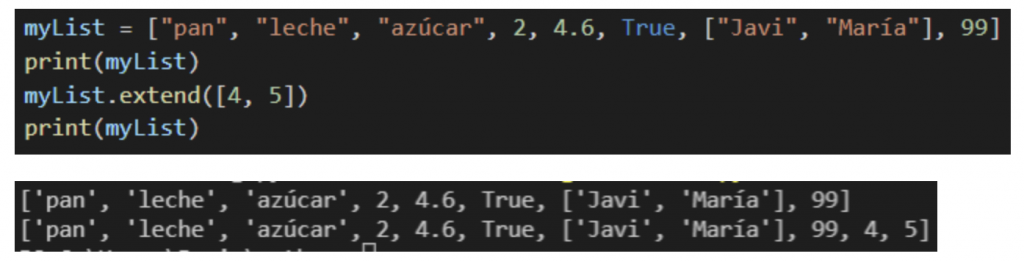
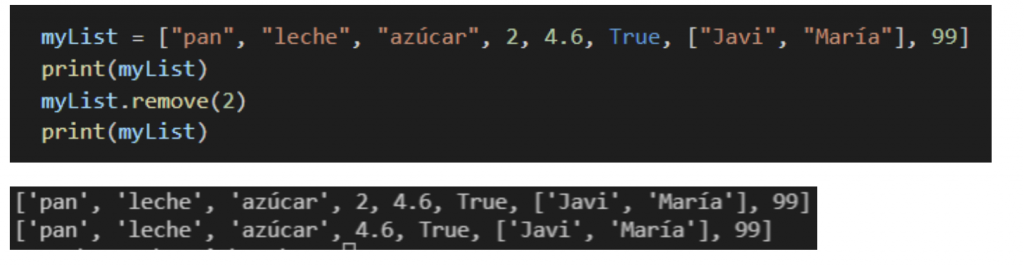
Remove()
With this method we can delete an item from the list indicating it as an argument. Remove() will only delete the first occurrence of the element.
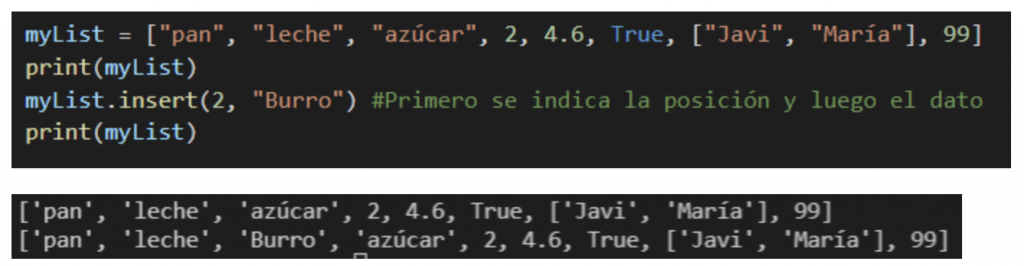
Insert()
With this method we can add an element to our list but unlike append(), we can insert it in the position we want within the index.





































Good day, can you tell me how to delete an element that is part of a list that is contained in the initial list. Thanks for your attention