In past articles on the blog, the scars of buildings were defined, this being a current and very important topic, we will deal with it more broadly, knowing the definition of thermal bridges and the energy losses that negatively impact the electricity bill and diminishing our economy.
To combat injuries in buildings, there are two groups of actions that require a short-term investment and that will translate into long-term profits by considerably reducing electricity consumption. It is important to emphasize that the final objective from a thermal point of view is to keep the user in comfort conditions (around 21ºC in winter and 25ºC in summer, with relative humidity in both cases of 50%) and with the lowest possible energy consumption.
To achieve these set conditions, the construction must face the external conditions of each locality by two means:
Passive energy systems
They are those measures that do not require energy consumption To act, they are based on a correct architectural design, the use of appropriate materials for each function and the correct construction method that will isolate the construction, we can divide them into:
Building thermal envelope: its enclosures with the exterior, land or non-air-conditioned spaces such as facades, roofs, floors, etc.

This section includes everything related to insulation, which can be divided into interior insulation and exterior insulation. At the same time, there is a wide range of materials on which the technical criteria for their use will depend.
Other passive measures also include a focus on the materiality of windows and doors, with window frames having a thermal break and the placement of double glazing to form an air chamber that will prevent the exchange of energy with the outside, other solutions. They include awnings, slats and the use of blinds or lattices that will help prevent energy dissipation.
Ventilation systems: They will be responsible for maintaining health conditions inside the building. We can mention passive heating strategies that will help save energy, such as cross ventilation, convective effect ventilation, and night thermal mass ventilation.
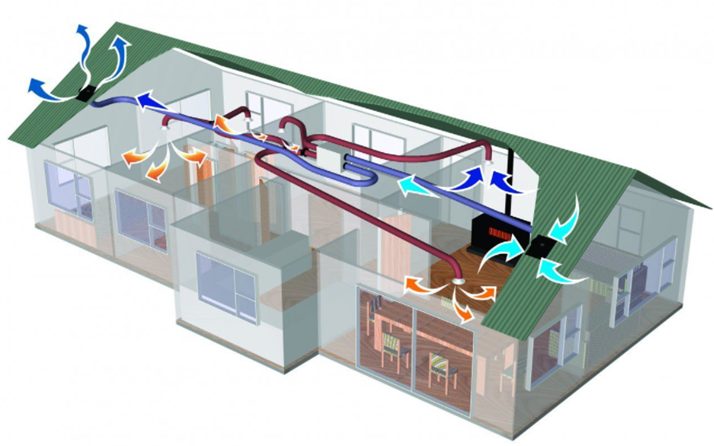
Representation of a ventilation system that allows exchange with the outside to comply with the renovations specified in the Technical Construction Code in its Basic Health Document (DB HS 3).
Orientation and solar collection: The way in which the building takes advantage of or is protected from solar radiation depending on the climate and time of year, this is the case of direct and indirect solar gains according to the position and orientation of the different environments according to their location, as well as The entrance to them constitutes an analysis of the building based on its rooms, where they could be located according to the best use and needs of the same.

Location of the facades whenever possible to the south for direct use of the sun.
active energy systems
They are the measures that require energy consumption to function, would be all specialized equipment such as boilers, cooling, heating and air conditioning systems that allow the passive measures of thermal insulation and ventilation control to be complemented by means of generation of heat or cold when necessary.

Underfloor heating powered by a heat pump, a heating system that is booming today.
As we can see, there is a lot of work to be done, in future blog articles we will begin by defining and detailing other modalities of thermal and acoustic conditioning and we will delve into the world of energy rehabilitation to adapt to the new regulations of the Technical Construction Code, the which is very strict on energy efficiency issues.
If you want to learn more about energy efficiency and become an expert in small and large scale renewable energy issues, don't miss the opportunity to sign up for our Master in Efficient Management of Renewable Energies



































