In previous weeks we talked to you about the reserved words or keywords, in that list of words “while” was included and we told you that it was used for loops, well, let's see How those loops work. If you want to perform programming jobs, you must train in this area and for that we recommend the Master of Advanced Programming in Python for Big Data, Hacking and Machine Learning in EIP.
Loop operation
As we can see in the diagram below, loop operation while it's simple, When we enter the loop, it is verified that the condition that we have indicated is met, if so the result of the verification of that condition will be true and instructions will be executed rechecking the condition when they have been completed.
If, on the other hand, the result of the condition check was False, the loop would end and no instruction would be carried out.
Let's see it with examples
- In the following code we will run a loop while so that it prints a countdown from 10 to 0.

In the code we declare the variable i with a value of 10, in the condition we indicate that as long as the value of 'i' is greater than or equal to zero it enters the loop and once inside the loop we print the value of 'i' and subtract one from it so that it goes down. Once 'i' is '-1', the condition is not met, so it would not enter the loop printing the message that the countdown has ended.
- In the following example let's make a loop while controlled by event.

The loop works as long as the user does not end it by entering a zero. We can see that the condition is that the number entered is different from zero.
- Now let's go combine a while loop with a 'else', unlike the conditional 'if', the complete block 'else' will always be executed when the loop ends while.

Starting from the previous example, We have added a new variable called 'sum' where we have been adding the numbers entered. Once the loop is finished, the sum variable will be printed.
- Now let's see an example of use of the sentence 'break' to end a loop.
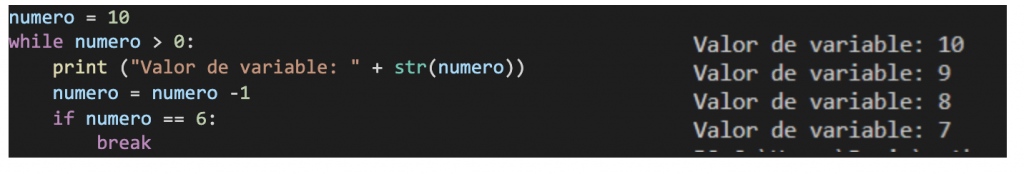
As we can see though the condition is met, when the number has the value of 6 we enter the 'if' and the sentence break It takes us out of it.
- Let's see now An example of the use of the continue statement.

In this last example, starting from the previous example, we see that when we reach the number 6 and enter the 'if', sentence continue makes it automatically jump to the beginning of the loop, ignoring the rest of the instructions and stopping printing the value 6.





































Thanks for sharing the knowledge.