By Elias Vallejo, professor “Data protection audits and information systems” in the master's degree in Compliance & Data Protection Directorate of the EIP International Business School wanted to share with us a study analyzing the different risks mentioned in the RGPD.
Different risk analyzes in the GDPR
Professor Elías Vallejo comments that the idea of carrying out a risk analysis in the RGPD is present in 3 cases.
- 24.- Responsibility of the Data Controller and Art. 35 Data Protection Impact Assessments
- 32.- Security of Treatment.
- 25.- Data protection from design and by default
In the first and second post of our Data Protection & Regulatory Compliance Specialists Blog, Elias Vallejo told us about the Art. 24, Responsibility of the Data Controller, Art. 35 Data Protection Impact Assessments and about him Art. 32, Security of Treatment.
We leave you the words of Elías Vallejo, about art, 25 Data protection from design and by default.
Art. 25.- Data protection from design and by default
The risk analysis in this article is broader than the previous two.
On the one hand, when mentioning that it must be taken into account “the state of the art” is already telling us that technical security measures must be considered; but, on the other hand, in accordance with article 25 itself, the application of technical and organizational measures must have the purpose of “comply with the requirements of this Regulation and protect the rights of interested parties”
But if you take into account security measures and possible legal breaches,
What differentiates it from art. 24?
The answer is not simple, but that does not mean we should abandon the idea of delimiting this risk analysis and differentiating it from the others.
The first difference is that the risks must be taken into account before creating the information system, from its design, which does not occur in the other two risk analyses.
Likewise, the controls to be included in this risk analysis are more detailed, they are not so general, “default” privacy must be considered, maximum privacy in all phases of the system.
In this risk analysis, pseudonymization and data minimization take on special importance (understanding the latter from a fourfold perspective: the amount of personal data collected, the extent of its processing, its retention period and its accessibility).
But everything explained in this analysis still leaves its application up in the air. We must go to the “Privacy by Design Guide” of the AEPD.
Traditionally, information security is protected, ensuring the confidentiality, availability and integrity of information. But that is already analyzed in the risk analysis of art. 32 which, in turn, is part of the risk analysis of art. 24 and the EIPD of art. 35.
In the risk analysis of art. 25, the risks of any deviation from what is planned and permitted by the Organization must be analyzed. This makes us begin its analysis based on the aforementioned Guide. Thus, three new concepts emerge with which we must work when carrying out this analysis of privacy risks from design and by default.
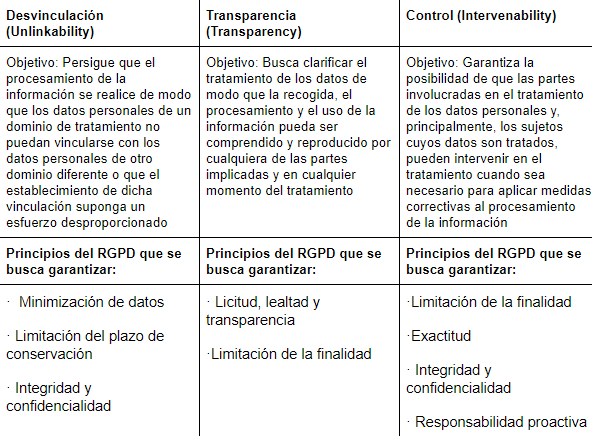
This risk analysis does not analyze probabilities and impacts, but rather establishes design strategies, then establishes tactics (describing them) and finally proposes controls through design patterns.
Design strategies
First, we have the data-oriented privacy design strategies: minimize, hide, separate, and abstract.
Second, we have the process-oriented privacy design strategies: inform, monitor, comply, and demonstrate.
However, this topic requires more detailed study that will not be addressed in this article.
Do you want to specialize in Compliance Management and data protection?
He Master in Compliance & Data Protection Management will make you a highly qualified professional with the necessary skills to carry out specialized tasks in two of the most relevant areas for both private businesses as for public administrations: data protection and regulatory compliance or Compliance.




































