In any modern environment, SAP APIs have the ability to integrate and connect systems, making them crucial for business success.
In this context, Application Programming Interfaces, better known as APIs, emerge as silent heroes, facilitating communication and data exchange between various applications. But what are APIs really? APIs in SAP And how can they transform your business? Join us on this journey to find out.

What are APIs in SAP?
APIs in SAP, which stands for Application Programming Interfaces, are sets of definitions and protocols that allow different applications to communicate with each other.

They act as intermediaries, facilitating interaction between systems by allowing one application to access the functionality or data of another without needing to know the internal details of its implementation.
How APIs work
To understand how APIs work, imagine you're a customer (the requesting application) who wants to order a Hawaiian pizza (a feature or piece of data). The person serving you (the API) takes your order and delivers it to the kitchen (the system providing the feature or data). After a while, they return with your pizza ready.
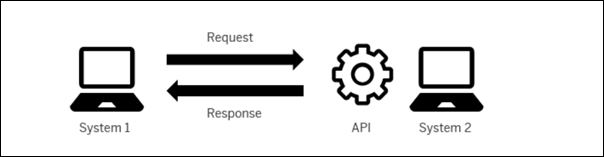
This process allows applications to interact in an orderly and efficient manner, without the customer needing to know how the pizza is made—that is, how the other system works.
Types of APIs
There are several types of APIs, each with specific characteristics and different uses:
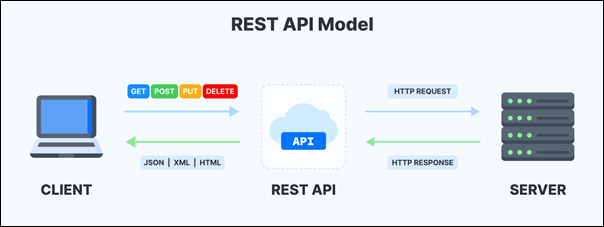
REST APIs (Representational State Transfer)
These are the most common and use the HTTP protocol to make requests and receive responses. Their simplicity and scalability make them ideal for web services and mobile applications.
OData APIs (Open Data Protocol)
Developed by Microsoft, these APIs extend the capabilities of REST APIs by adding a layer of standardization and functionality that makes it easier to create and consume REST APIs.

OData is especially useful for applications that handle large amounts of data and require dynamic access to it, and is widely used by SAP.
SOAP APIs (Simple Object Access Protocol)
These APIs use the HTTP or SMTP protocol and are more complex than REST APIs. They are suitable for business applications that require a high level of security and complex transactions.

Other Types of APIs
In addition to those mentioned, there are other types of APIs that adapt to various needs such as;
GraphQL APIs
They allow clients to request exactly the data they need, reducing the amount of data transferred and improving efficiency.
They are useful in applications with complex data requirements.
Library APIs
They provide access to specific functions within a software library, facilitating code reuse and the implementation of common functionalities.

Using APIs in SAP
SAP has widely adopted the use of APIs to improve the integration and functionality of its solutions.
SAP APIs allow companies to seamlessly and securely connect their SAP systems to other applications and services, both internal and external.
Benefits of APIs in SAP
- Simplified Integration: APIs allow SAP to easily integrate with other systems, eliminating the need for complex and costly custom development.

- Flexibility and Scalability: Companies can adapt and scale their SAP solutions to their specific needs, adding or modifying functionality without affecting the core system.
- Accelerated Innovation: By facilitating integration with new technologies and services, APIs enable businesses to innovate more quickly and stay competitive in an ever-changing marketplace.
- Improving User Experience: APIs allow you to create more intuitive and personalized applications, improving the end-user experience.
Examples of API Use in SAP
SAP API Business Accelerator Hub
It is a platform that offers a wide range of predefined APIs that companies can use to integrate their SAP systems with other applications and services.
These APIs cover various functional areas, such as finance, human resources, sales, and more.
SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI)
Use APIs to connect cloud and on-premise applications, facilitating business process integration and real-time data synchronization.

SAP Fiori
It uses APIs to provide a modern and consistent user experience across all SAP applications, enabling developers to create customized and optimized user interfaces.
Conclusion
APIs are a powerful tool that enables applications to communicate and collaborate efficiently. In the context of SAP, APIs play a crucial role in system integration, flexibility, and innovation. By leveraging APIs, companies can improve their processes, offer better user experiences, and remain competitive in a dynamic business environment.

The adoption of APIs in SAP not only facilitates integration and scalability, but also opens up a world of possibilities for innovation and continuous improvement. Ultimately, APIs are the gateway to a more connected and efficient future, where technology becomes a strategic ally for business success.
Discover our SAP training
Find out everything on our blog and train in SAP with our Sap S/4Hana Finance Official Certificate.


































