Dealing with a cyber incident
The massive implementation of technology in our lives, in addition to clear benefits from both a personal and professional point of view, brings with it a significant set of challenges, an incident could impact our personal lives or the operations of small businesses.
Traditionally, cyber incident management has focused on defining complex processes, within the reach of large companies.
This article explains how to apply the principles associated with managing these incidents in our homes or small businesses, exploring the potential vulnerabilities and risks, impacts and practical steps that can be implemented to protect digital assets in these cases and, where appropriate, manage a incident.
Vulnerabilities in the home and small businesses
Home and small business networks, applications, and the digital information we create and manage have become the center of our "digital existence." These networks interconnect and allow us to access devices as diverse as phones, computers, storage drives, smart appliances, home automation sensors, cameras, payment terminals, and more.
Unfortunately, this massive and continuous interconnectedness also It brings with it the emergence of vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals..
The main attack vectors that can be used to trigger a cyber incident at home or in a small business are:
• Phishing attacks.
• Introduction of malware/ransomware
• Use of IoT devices with limited security capabilities.
• Unsecured and shared Wi-Fi networks.
• Low level of protection on devices.
• Social Engineering (deception, threats, etc.).
The exploitation of these attack vectors can have serious personal and professional consequences, the main ones being:
• Data loss.
• Financial loss
• Emotional impact
• Loss of privacy.
• Damage to reputation.
Reducing the risk
The first step that should be taken in order to reduce the risk of suffering a cyber incident in our home or small business is Be aware of the devices we have, the information or services they manage and how and to which data networks they connect..
Often, we have no specific knowledge of how many devices we have connected to our networks, both at home and in small businesses (phones, tablets, storage units, computers, applications, sales terminals, cameras, home automation devices, routers, televisions, etc.), what visibility they may have, and what information they contain.
For example, if our children's friends come over, do they connect their devices to the same Wi-Fi network as our own devices? Do we share the same Wi-Fi network at home with our work computer, appliances, and home automation devices? In the case of small businesses, do we offer Wi-Fi to external clients or staff on the same network as the company's devices—payment terminals, computers, etc.—are connected? Do we regularly change the connection passwords for the Wi-Fi networks we offer?
All these actions introduce real risks that can cause incidents.
To prevent cyber incidents from occurring, it's important to implement some basic measures to strengthen security and minimize the potential impact:
- Identify what our digital assets are and the information they manage/store, and monitor its use and what information is shared. This will help us detect potential incidents early, be aware of their impact, and what contingency measures to implement. Do we know how many devices we have connected to our networks? What information is stored on them? Who has the access keys? What would happen if a device were lost or stolen? What is it used for? What is shared?
- Raise awareness among both your own family and employees about the risks, creating a climate of trust that allows you to report any suspicions in this area. Stay informed, to the extent possible, about current cyber threats and trends. There are multiple online resources, as we'll detail later.
- Strengthen Passwords. Use strong, unique passwords for each account and enable two-factor authentication when available. Use words or phrases that combine letters, numbers, and symbols. Always change the default passwords used on the devices you use.
- Update the Software Regularly. Keep your devices, operating systems, and applications up to date.
- Wi-Fi Network Security. Securely configure your network. Change the router's password (usually found on a sticker on the router itself). Use a complex Wi-Fi password and create separate networks for different uses (guests, home automation devices, retail terminals, etc.).
- Be alert against direct attacks such as phishing, vishing, or smishing by being cautious when clicking on links or opening attachments in emails or SMS messages, especially from unknown senders, and by being wary of unexpected phone calls.
- Install firewall and antimalware. Install and regularly update firewall and antivirus software on your devices to protect them.
- Security in home automation devices (IoT)Change the default passwords on your home automation devices and make sure they have the latest firmware updates.
- Make backup copies of your dataRegularly back up your important data to a secure hard drive/external storage unit or cloud storage service.
- Make payments online, especially on unknown sites or new stores, using reloadable prepaid cards or with cards associated with bank accounts where the available balance is limited.
Cyber incident management
Cyber incident management has traditionally been understood as an activity specific to large companies, where specific procedures and organizational structures are designed and implemented.
Even if this is not possible in small businesses (and of course in the domestic environment), it does not mean that one should not take into account how a possible incident must be managed, putting in place appropriate measures to prevent it and minimize the impact it may have.
The traditional incident management process consists of different phases, and while all are necessary, some may be included as part of others or handled simultaneously.
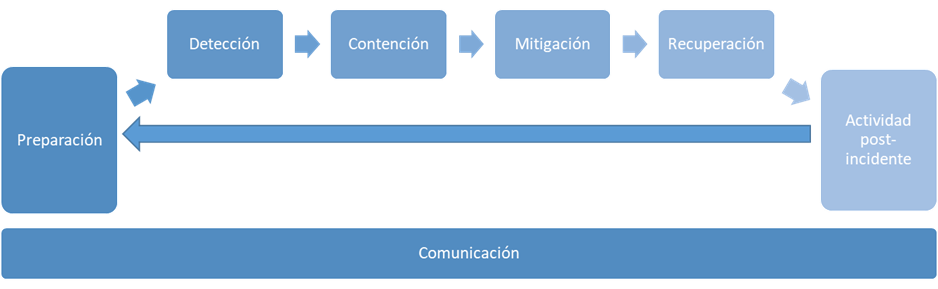
But how do you apply each of these phases to small businesses or the home environment?
Preparation
Possibly the most important phase when dealing with incidents is preparation. This will help us avoid them and limit the impact of any that may occur.
As a first basic, as indicated in the point on risk reduction, basic protection measures must be implemented in the systems and devices used. Let's briefly review the most important ones.
- Identify our digital assets and information and watch its use.
- Raise awareness.
- Strengthen Passwords.
- Update the Software.
- Securely configure your networks Wi-Fi.
- Be alert and distrust.
- Install firewall and antimalware.
- Security in home automation devices (IoT).
- Make Backups of your data.
- Control online payments.
Regarding identification, it is important to carry out a reflection on our assets and their useWe must be aware of the digital assets we use and their importance. This way, we can consider what alternatives we have when handling an incident. To do this, we can ask ourselves some of the following questions (adapted to our specific case):
- If we lose our phone, do we have a copy of the photos or information it stores? Is access to it protected/locked? Do we have any "important" information stored on it?
- If we lose access (due to a breakdown, infection) to the computer we use to manage our small business (PC, laptop, etc.) or the one we work on at home, do we have a copy of the information stored there? Would we be able to recover it? Do we have maintenance contracts for the management software we use?
- Do we use the same computer (laptop) for business management and for client visits? If that computer is stolen, could the business continue operating?
- Do we securely store login credentials for the devices and accounts we use to manage our business or family accounts? Do we keep an inventory of the active service accounts?
- Are we aware of and use the privacy settings on the social media and online services we use? Are we aware of who we (or our family members) share online content with and what type of content is shared?
It is also very important to basic cybersecurity training and awareness, there are many resources available that can be used by both small businesses and in the home environment. For example, National Cybersecurity Institute (INCIBE) offers a multitude of material:
https://www.incibe.es/empresas/formacion/kit-concienciacion
https://www.incibe.es/ciudadania/formacion/guias
Among the guides offered are the following:
- How to create a backup
- Cybersecurity Guide. Cybersecurity within everyone's reach
- Guide to managing your security and privacy with Google
- Guide to configuring the Wi-Fi router
- Cyberattack Guide
- Guide to setting up mobile devices
- Web Browser Guide
- Guide to learning how to identify online fraud
- Guide to safe online shopping
Similarly, INCIBE offers basic courses for small businesses and the self-employed at the following link:
https://www.incibe.es/empresas/formacion/ciberseguridad-para-micropymes-y-autonomos
From a domestic perspective, in addition to all the resources listed above, INCIBE offers specific resources to share with children at the following links:
https://www.incibe.es/menores/recursos
https://www.incibe.es/menores/familias/ciberseguridad
In the case of families, and especially with minors, it is essential to cultivate a relationship based on trust with them, so that in problematic situations they feel comfortable coming to us or another trusted adult without fear of our possible reaction. It is also important to strive to be a role model through our online behavior. It is inconsistent to require them to be responsible in their use of mobile devices and social media if we ourselves fail to fulfill that responsibility.
ID
In this phase, any anomalies regarding devices or information are detected. All employees and family members should be encouraged to openly report any unusual behavior they detect in the use of electronic devices or online information, as this may be an indication that a potential incident is underway.
Early identification will limit the impact of any incident.
In the case of families, and especially minors, it is essential, on the one hand, as explained in the preparation phase, to create a climate of trust that facilitates this communication and, on the other hand, to maintain active monitoring of their use of devices and information.
Containment and mitigation
If an attacker has managed to compromise a device, our information, our online accounts, etc., we must try to prevent them from spreading the compromise, limiting its potential impact.
If it hasn't already happened, it's likely that actions taken from this point forward could affect our available information, the provision of our company's services, or even our personal lives.
Some of the actions that can be taken first, always depending on the identification carried out, may be:
• If the origin of the incident is in a computer connected to our network, disconnect it.This can be done, if it's a standalone device, by disconnecting the network cable or disabling the wireless link if the connection is via Wi-Fi.
• Identify the availability of backups of the information contained in the affected devices or accounts.
• If the technical details of the type of cyber incident are known and the necessary knowledge is available, they can be applied containment measures more tailored to each situation (blocking certain emails, applying firewall rules, blocking access to shared folders, etc.).
• Change passwords access to online services that may be affected/involved in the incident, activating two-factor authentication on them as far as possible.
• Take screenshots, photographs of the aspects that we consider relevant or identifying the incident, since they may be necessary in a hypothetical subsequent investigation.
• In the case of theft or damage, once the extent is known in detail, cContact our insurance company.
• For cases of publishing/sharing personal content such as images or data, inform the points of contact security measures from website providers, social networks, etc. to prioritize the removal of such content.
• Contact other entities that can offer assistance or participate in the resolution. Internet service providers can apply filters or activate protection measures, companies with which we have maintenance contracts can offer guides and assistance, and organizations such as INCIBE can offer additional information and assistance. In the event of loss or theft, or if a deliberate attack is identified, the incident should be reported to the appropriate authorities.
If the incident involves educational or sports centers, contact them. The section on communication below offers advice and contact information for this matter.
Once initial steps have been taken to contain the problem, it's time to continue implementing measures to mitigate the impact of the incident.
If the incident involves devices or systems, the most drastic mitigation measure usually begins with a secure erase/format of the compromised storage media and a reinstallation of the systems, but unfortunately, this isn't always possible; in some cases, because there isn't a recent backup of the information, and in other cases, because reinstalling a system without knowing the cause of the incident can cause the problem to recur.
It should be noted that anti-malware product manufacturers and response teams offer solutions to remove threats from compromised computers. These solutions must first be identified by the manufacturer so they can be automatically detected and removed.
Whether you are performing a new installation or restoring a backup from before the cyber incident, it is necessary apply the necessary security measuresThis includes updates to both the operating system and other applications. It's also necessary to analyze the cause of the incident in order to implement measures to prevent it from recurring.
When backups are unavailable and a complete system reinstallation has been performed, the necessary information must be manually extracted from the previously compromised computer/device and transferred to the new system, taking care not to transmit the infection along with it.
If it is an incident associated with online accounts, as indicated, it is essential to change the access password for them (and all services that share credentials) and, if possible, activate two-factor authentication.
Recovery
The purpose of the recovery phase is to recover the functionality available on systems or devices before the incident occurred.
Depending on the incident, this will involve various actions, ranging from purchasing new devices, formatting and reinstalling systems and applications, recovering data backups, or even assuming the loss of information and the consequences this loss may have.
It's important to pay special attention and monitor devices and systems for any signs of suspicious activity that may indicate the problem is recurring.
If the incident involves the publication of data or images on social media or websites, it is important to periodically monitor their possible re-publication by conducting periodic internet searches.
Post-incident actions
Once the incident is under control and business has returned to normal, it's time to carry out a process that often gets overlooked: lessons learned.

It is necessary to analyze and reflect on what happened, identifying the causes of the problem and how the activity has developed during its management.
The purpose of this process is to learn from what happened and take appropriate measures to prevent a similar situation from happening again. It is important to involve all staff and/or family members who may have been involved in this process so that the learning process reaches everyone and leads to overall improvement.
Communication
As previously stated, communication is key, both in preparation, building trust, and raising risk awareness, as well as throughout incident management.
In addition to what was expressed in the preparation phase, in the event of a situation that we cannot directly control, it is a good idea to contact INCIBE, using the "Your Help in Cybersecurity" service through telephone number 017, WhatsApp 900116177 or the form https://www.incibe.es/linea-de-ayuda-en-ciberseguridad/formulario017.
In this service, they will offer us guidance on possible next steps and contacts we can use.
The Spanish Data Protection Agency also offers a priority channel on the following website https://www.aepd.es/es/canalprioritario where any violations related to personal data can be reported.
The need to report the incident to law enforcement agencies should be analyzed in the event of a possible crime.
To this end, the national police offers the next web, which details the reporting process.
Likewise, if minors are involved and the incident may be related to an educational center, sports club, etc., their guardians should be notified.
Conclusion
The convenience brought by the digital world we live in is intertwined with the complexity of cybersecurity, making cyber incident management a necessity.
While cyber incident management processes have traditionally been developed for large companies using dedicated teams, the same management phases can be implemented in home or small business environments.
Protecting our homes and businesses goes beyond physical protection.; now involves safeguarding our online presence. By promoting active digital awareness, including the implementation of basic protection measures both at home and in small businesses, the likelihood of cyber incidents can be significantly reduced.
Finally, communication is an essential component of cyber incident management, and it is necessary to identify potential stakeholders who may be involved in cyber incident management.



































